Now let’s try to manage it from outside the cluster with kubectl. There are several options. As I did not have a ready Linux VM I tested first with Windows. All options can be found here.
Windows
Open a command prompt as administrator and type
winget install -e --id Kubernetes.kubectlClose the window and open a powershell window
cd ~
mkdir .kube
cd .kube
New-Item -type file -name config
notepad .\configLeave the window open and let’s get the kube config from the cluster. SSH to one of the nodes and
sudo cat /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yamlCopy the contents to the notepad and replace on the server: line, 127.0.0.1 with your FQDN or the IP address of the Load Balancer
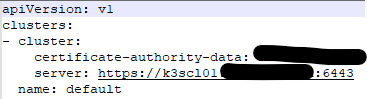
Save the file as C:\Users\Username\.kube\config
Open a powershell window
kubectl get nodes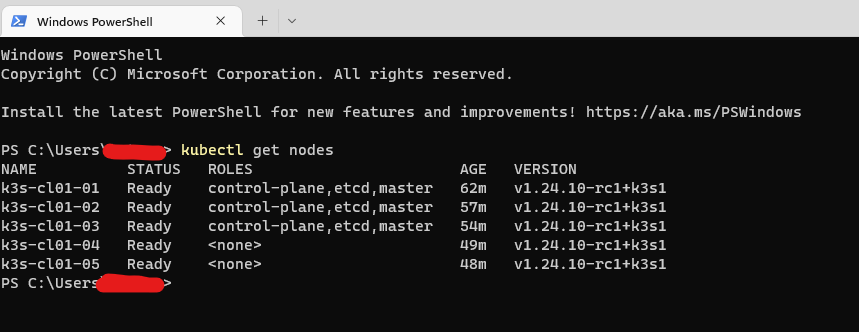
In case you have done something wrong with your certificate use the alternative command
kubectl get nodes --insecure-skip-tls-verifyUbuntu
As this will be the main point of administration for the cluster(s) lets give it some love by installing zsh to replace bash. So SSH into the Admin node, get sudo privileges and
apt install zsh -yand replace bash by installing the oh-my-zsh plugin. (Do not forget to reply yes on the question to replace the default shell.
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)"
Now let’s install kubectl
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl By using zsh we can enable autocompletion to the kubectl commands which can be very useful. So let’s edit the zsh config file
nano ~/.zshrcAnd add
source <(kubectl completion zsh)If you are going to manage a single cluster with a single namespace you can skip this step. But it you never know so let’s install also kubectx and kubens
git clone https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx /opt/kubectx
ln -s /opt/kubectx/kubectx /usr/local/bin/kubectx
ln -s /opt/kubectx/kubens /usr/local/bin/kubensSince we are using oh-my-zsh
mkdir -p ~/.oh-my-zsh/completions
chmod -R 755 ~/.oh-my-zsh/completions
ln -s /opt/kubectx/completion/_kubectx.zsh ~/.oh-my-zsh/completions/_kubectx.zsh
ln -s /opt/kubectx/completion/_kubens.zsh ~/.oh-my-zsh/completions/_kubens.zshEdit again the zshrc file
nano ~/.zshrcand add
autoload -U compinit && compinitNow time to add the configuration file
On one of the server nodes
sudo cat /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yamlCopy the contents and on the admin node
nano ~/.kube/configAnd replace default with the name of the cluster
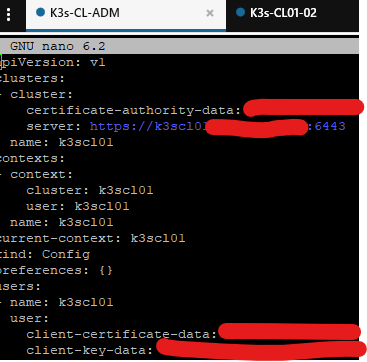
Save and exit
Time to try some commands.
kubectl get nodes
kubectx
kubens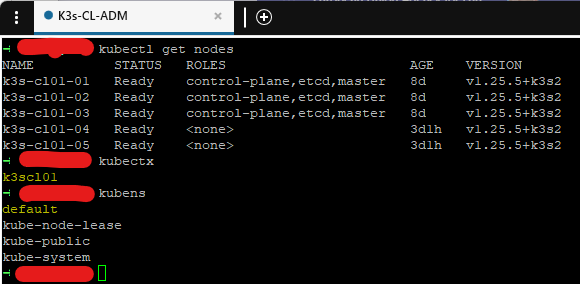
Looks good. Now one more tip in order to see the context and the name space connected to in the command prompt
sudo su
cd ~
nano .zshrcand add kube-ps1 in the plugins to be activates like in the picture bellow
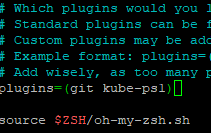
And in the end of the file add the following line
PROMPT='$(kube_ps1)'$PROMPTSave and Exit
Give it a try
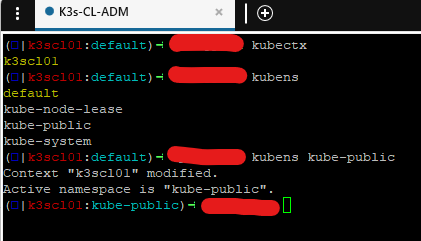
HELM
Helm is necessary to install Rancher so lets install it on our Administration node
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.shAdd the rancher, jetstack and bitnami repositories, I suggest the stable one but it is up to you to decide. Then, update the repositories
helm repo add rancher-stable https://releases.rancher.com/server-charts/stable
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
help repo updateOne last thing regarding the Admin node. The config file should only be accessible with root previleges so if you get
WARNING: Kubernetes configuration file is group-readable. This is insecure. Location: /root/.kube/config
WARNING: Kubernetes configuration file is world-readable. This is insecure. Location: /root/.kube/configthen run the command
chmod go-r ~/.kube/config